Romps, Heat index extremes increasing several times faster than the air temperature, ERL, 2024
Media coverage
Heat index
Heat index in °F
Heat index in °C
See Lu and Romps, 2022 for details.
Paper
Corrigendum
Print coverage
Description
The heat events of summer 2023 broke many records, but it remains a challenge to communicate the exacerbation of such events by global warming. Using Texas as a case study, it is shown here that global warming has led the highest heat index values to increase several times faster than the air temperature. In particular, it is estimated here that global warming has increased the highest heat index values in Texas by, on average, about 8 to 11 °F. Unfortunately, these large increases signal an approach to hyperthermic conditions.
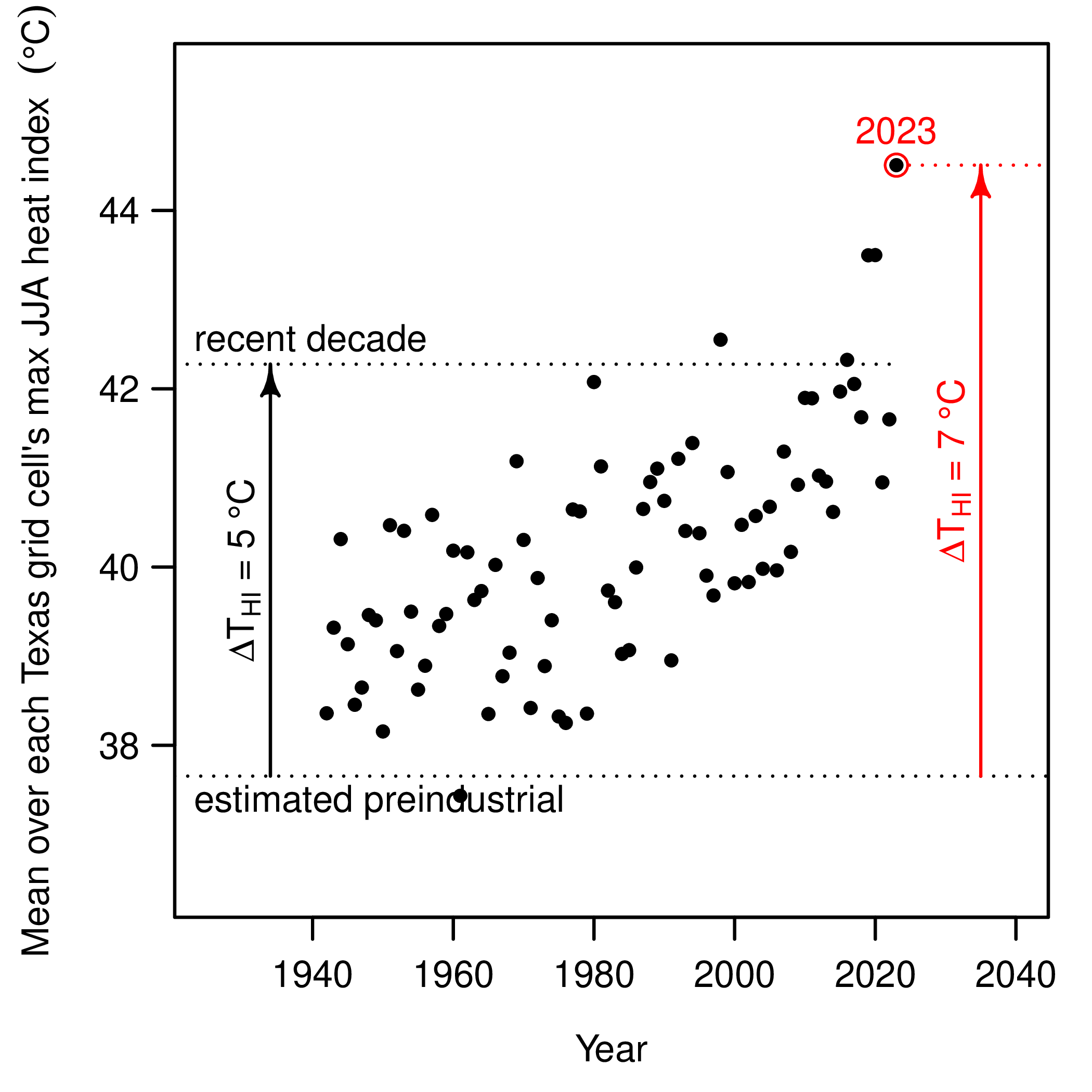
For every year, the spatial average over Texas of the local maximum heat index in degrees Celsius (note that 5 °C is about 9 °F and 7 °C is about 13 °F). The top dashed line marks the mean of the data points 2014-2023. The lower dashed line marks the estimate of the preindustrial value.